A GUI tool for end-to-end creation of Win32 Apps in Microsoft Intune.
This post provides details of “Show-Win32AppUI”, a GUI tool that simplifies the end-to-end process of creating Win32 Apps in Intune.
The GitHub source is available here. Instructions for setup and use are below.
This isn’t a one size fits all community tool. You will likely need to modify it to meet your needs. However, its written in PowerShell and has code comments and blog posts to make editing simpler.
SETUP
Modules
Show-Win32AppUI depends on two PowerShell modules. Install these modules if you don’t already have them.
Install-Module -Name MSAL.PS
Install-Module -Name IntuneWin32App
The most recent tested versions are listed below:
Install-Module -Name MSAL.PS -RequiredVersion 4.37.0.0
Install-Module -Name IntuneWin32App -RequiredVersion 1.4.0
Tenant ID
Update the $TenantID on line 4 of Show-Win32AppUI.ps1 to use your required Azure tenant. Your tenant ID is available from the Azure AD portal Overview page.
Azure Client App
An Azure Client App is used with interactive authentication to access the Microsoft Graph. There are two setup steps required:
- Specify the Azure application
By default, the tool will use the built-in Microsoft Graph PowerShell enterprise application. However, I recommend creating a custom Azure app in your own tenant. A step by step guide to creating a custom app is available here.
If using a custom app, update Show-Win32AppUI.ps1 to set the $ClientID variable on line 6 to match the client ID (a.k.a Application ID) of your app.
- Consent to the required permissions on behalf of your tenant
Whether you use a custom app or Microsoft Graph PowerShell, the app must be configured with the required API permissions and consent must be granted. The delegated permissions are listed below. A step by step for setting these permissions can be found in the second part of this article.
- Directory.AccessAsUser.All
- DeviceManagementApps.ReadWrite.All
- Group.ReadWrite.All
- GroupMember.ReadWrite.All
- User.Read
User permissions
Delegated consent uses the intersection of application permissions and user permissions to authorise access. i.e. the authenticated user must have the required permissions as well as the application. When using the app, authenticate using an Azure account with one of the following roles:
- Intune Administrator
- Global Administrator
Workstation permissions
The tool does not need administrative access to the client workstation. Internet access is required, to download the Win32 Content Prep tool on first use.
PowerShell script execution
PowerShell script execution is disabled on Windows clients by default. Use one of the methods below to allow script execution on the workstation.
set-executionpolicy Unrestricted
or
powershell -executionpolicy bypass -file <path to script>
Launch the tool
Start a PowerShell 5.1 or Pwsh 7.x console and execute the script as follows:
.\Show-Win32AppUI.ps1
To show debug information in the console add the WriteHost switch:
.\Show-Win32AppUI.ps1 -WriteHost
Using the tool
Page1 - PackageUse the file dialog to select the main Setup File - .msi, .exe or .ps1.For an .msi file, the setup and uninstall automatically uses MSIEXEC, defaulting to a quiet install/uninstall and verbose logging. For an .exe file, the setup parameters default to /S, but you should check the vendor information and replace this as appropriate. For a .ps1 file, setup and uninstall defaults to -noprofile and -executionpolicy bypass. The package source folder is the folder containing the setup file. All the files in this folder are packaged into an .intunewin file in a later step. The tool creates installation wrapper scripts called install.ps1 and uninstall.ps1 in the package source folder. Existing files with these names are overwritten. The Next button is only available when required fields have been completed. |  |
Page2 - DeploymentThe Display Name is built from the Publisher, App Name, Version and Package Number. If the language is changed from the default or the Bitness is changed to x86, these are also included in the Display NameFor .msi and .exe files, the fields are populated with information from the setup file, but can be edited as required. If there is already an Intune application with the same Display Name a warning will appear in the status bar. The simplest solution is to increment the Package Number. The Next button is only available when required fields have been completed. | 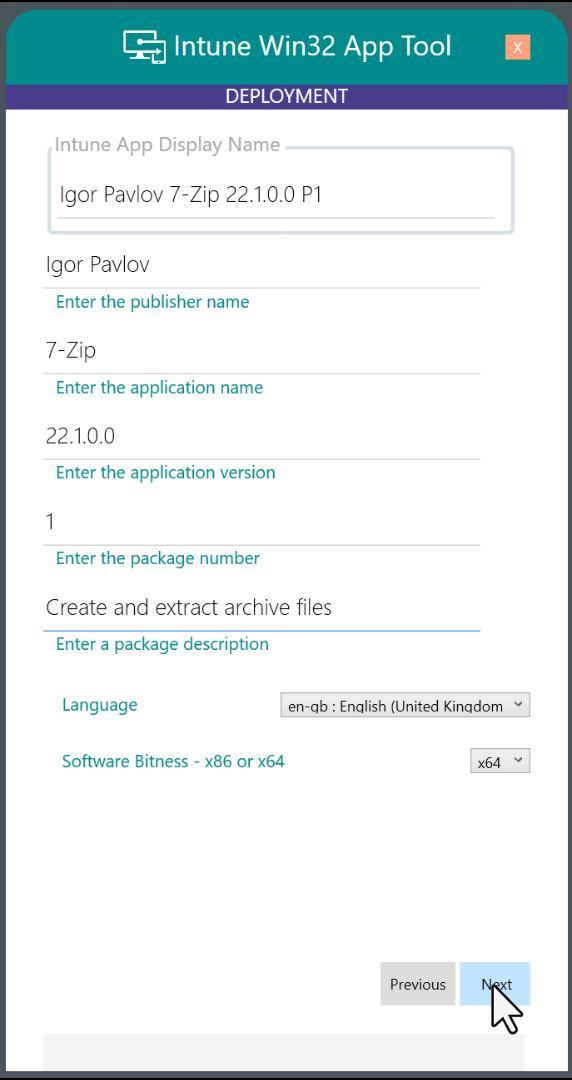 |
Page3 - AssignmentAssignment Groups shows the names of three AAD groups for Required Install, Available Install and Uninstall. The group name suffix is based on the App Name from Page 2 and cannot be edited here.The Owner must be a UPN of an AAD user. Start typing a name in the top box to see a list of options. Select a name and click Add. The Owner is set on the properties of the Win32App and the AAD groups. The Dependency and Supercedence lists are populated with existing Win32 Apps. Select from the list if these options are needed. Currently you can only select one of these options due to a limitation in the IntuneWin32App module. Click on the Logo box to select a image file for display with the application in the Company Portal. The Next button is only available when required fields have been completed. |  |
Page3 - ImplementThe final page follows a step-by-step approach to creating the Win32 App.Create Wrapper Scripts creates an install.ps1 and uninstall.ps1 file in the package source folder. Create Intunewin Package uses the Win32 Content Prep Tool to build an .intunewin file in the Output Folder. Create App Groups creates three AAD groups for Required Install, Available Install and Uninstall. If the groups already exist they are re-used. Create Win32 App creates the Win32 App in Intune and uploads the .intunewin file. This step can take some time depending on the package size. Configure Dependency / Configure Supercedence modifies the Win32 App in Intune. These steps are skipped if they are set to None. Configure Assignment modifies the Win32 App in Intune to add the assignment groups created in the earlier step. |  |
Troubleshooting
The tool creates a debug log on every run with detailed information and error messages. The default LogFolder is C:\Temp, but can be modified on Line 8 of Show-Win32AppUI.ps1.
The -WriteHost switch will also show the debug output in the console.
.\Show-Win32AppUI.ps1 -writehost

Options
The variables section in Show-Win32AppUI.ps1 allows default settings to be modified. The following section is at Line 50:

Detection Method
The Win32 app detection is hardcoded to use a file exists method. The Install.ps1 script wrapper creates a “.ps1.tag” file under the %PROGRAMDATA% folder and Uninstall.ps1 deletes it - a detection method first suggested by Michael Niehaus
Credits
Show-Win32AppUI is a front-end to the excellent IntuneWin32App module. Full credit to the contributors of this project.
The MSAL.PS module has simplified the transition from ADAL to MSAL authentication.
Boe Prox for PowerShell Runspace tips
SMSAgent for PowerShell WPF tips
This article was originally posted on Write-Verbose.com